Aurignacian Tool Industry
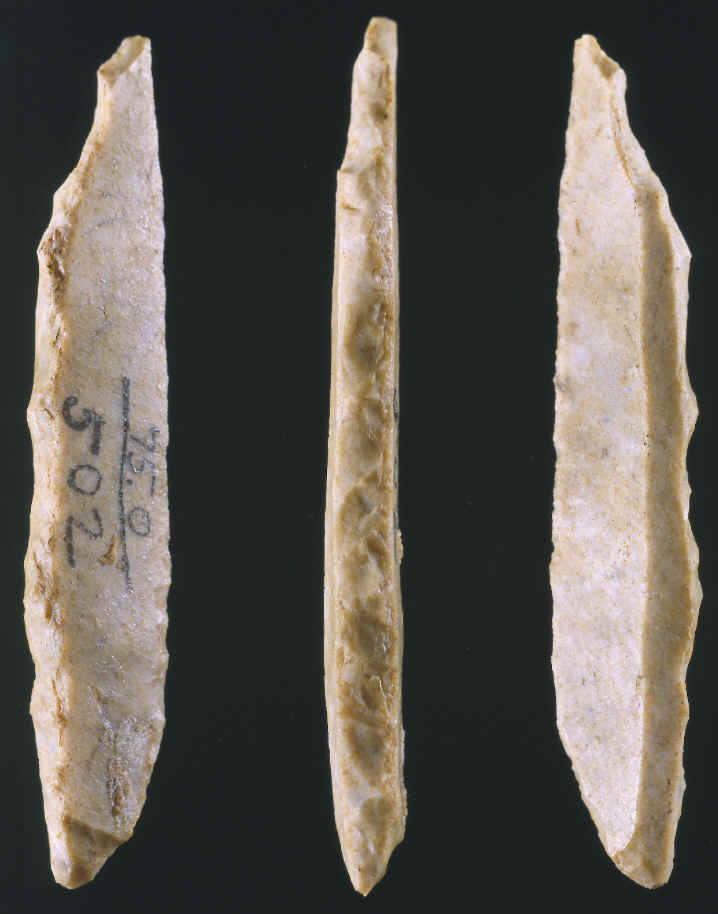
Pictures and descriptions of the Aurignacian tradition and their blade tools. Aurignacian definition, of, belonging to, or typical of an Upper Paleolithic industry with characteristic stone and bone artifacts that is distributed from western.
• (50,000–40,000 bp) • (46,000-42,000 bp) • (~44,500 – 36,000 bp) • (43 ka) • (46-43,000 – c. 26,000 bp) • (42,000-18,000 bp) • (36-18 ka) • (35–20 ka) • (33–24 ka) • (32–20 bp) • (24,000 - 15,00 bp) • (22–17 ka) • (22,000-14,000) • (21,000-12,000} • (20-10 ka) • (20,000-10,000 bp) • (~20,000-10,000) • (18,000 – 12,500 bp) • (17–12 ka) • (16,000-8,000 bp) • (15,500-13,100 bp) • (15,000-5,000 bp) • (15,000 BP — 11,000 bp) • (15,00 -11,00 bp) • (14,500–11,500 bp) • (14–13 ka) • (13–12 ka) • (11–8 ka) ↓ ↓. Entrance to the, a cave in the Eastern, where the remains of a human residence dated to the Aurignacian (40,000 to 30,000 ) were found by in the 1920s and 1930s. It was the first high-altitude Aurignacian site to be discovered that significantly influenced the knowledge of the culture The Aurignacian ( ) is an of the that is thought to have originated from the earlier Levantine culture. It is associated with the earliest modern humans in and their migration from the. It first appeared in Eastern Europe around 43,000, and in Western Europe between 40,000 and 36,000 years BP. It was replaced by the around 28,000 to 26,000 years ago.
The is,, south-west. The oldest undisputed example of human, the, comes from the Aurignacian. It was discovered in September 2008 in a cave at in in. Ableton Live 9 64 Bit Sylenth1. The site is one of the earliest known Aurignacian burials. Contents • • • • • • • • • Main characteristics [ ] The Aurignacian tool industry is characterized by worked or points with grooves cut in the bottom. Their flint tools include fine and bladelets struck from prepared rather than using crude. The people of this culture also produced some of the earliest known, such as the animal engravings at and the paintings at in southern France.
They also made,, and beads, as well as three-dimensional figurines., thought to be spear throwers or shaft wrenches, also are found at their sites. Association with modern humans [ ] The sophistication and self-awareness demonstrated in the work led archaeologists to consider the makers of Aurignacian the first in Europe. Human remains and Late Aurignacian artifacts found in juxtaposition support this inference.
Although finds of human skeletal remains in direct association with Proto-Aurignacian technologies are scarce in Europe, the few available are also probably modern human. The best dated association between Aurignacian industries and human remains are those of at least five individuals from the in the, dated by direct radiocarbon measurements of the skeletal remains to at least 31,000–32,000 years old. At least three robust, but typically anatomically-modern individuals from the cave in, were dated directly from the bones to ca. Although not associated directly with archaeological material, these finds are within the chronological and geographical range of the Early Aurignacian in southeastern Europe. On genetic evidence it has been argued that both Aurignacian and the Dabba culture of North Africa came from an earlier Aurignacian culture of the Levant.
Art [ ] Aurignacian figurines have been found depicting faunal representations of the time period associated with now-extinct, including,, and, along with anthropomorphized depictions that may be interpreted as some of the. Many 35,000-year-old animal figurines were discovered in the in Germany. Callan Method Stage 8 Download on this page.
One of the horses, amongst six tiny mammoth and horse ivory figures found previously at Vogelherd, was sculpted as skillfully as any piece found throughout the Upper Paleolithic. The production of ivory beads for body ornamentation was also important during the Aurignacian.
There is a notable absence of painted caves, however, which begin to appear within the. Typical statuettes consist of women that are called. They emphasize the hips, breasts, and other body parts associated with fertility. Feet and arms are lacking or minimized. One of the most ancient was discovered in 2008 in the in Germany.
The figurine has been dated to 35,000 years ago. Aurignacian finds include bone. The oldest undisputed musical instrument was the Hohle Fels Flute discovered in the cave in Germany's in 2008. The flute is made from a vulture's wing bone perforated with five finger holes, and dates to approximately 35,000 years ago. A flute was also found at the Abri Blanchard in southwestern France.
Bone flute, one of the oldest music instruments ever known (age: 35.000 - 40.000 year old, Tools [ ] from the Aurignacian culture are known as Mode 4, characterized by blades (rather than flakes, typical of mode 2 and mode 3 ) from prepared cores. Also seen throughout the is a greater degree of tool standardization and the use of and for tools. Based on the research of scraper reduction and paleoenvironment, the early Aurignacian group moved seasonally over greater distance to procure reindeer herds within cold and open environment than those of the earlier tool cultures.